SEO 101: The Beginner's Guide to SEO Basics
If you're new to search engine optimization (SEO), this is the place for you. In this beginner's guide, we'll cover all the SEO fundamentals you need to know to get started.
You may be here because you're planning on hiring an SEO specialist and you want a better understanding of how all of this works before choosing which SEO expert to go with. After all, there are a billion SEO firms to choose from.
Maybe you're here because you want to do your own content marketing and you want to become an SEO expert yourself.
Whatever reason brings you here, by the end of this “ultimate guide," I hope you have a better understanding of this digital marketing world, SEO best practices, how to tell the difference between good SEO and bad, and create a strategy that has you ranking in the search engines.
SEO Articles on noahgerman.com
- Local SEO Tips for Small Businesses
- The SEO Benefits of Blogging
- SEO Keywords: Common Misconceptions
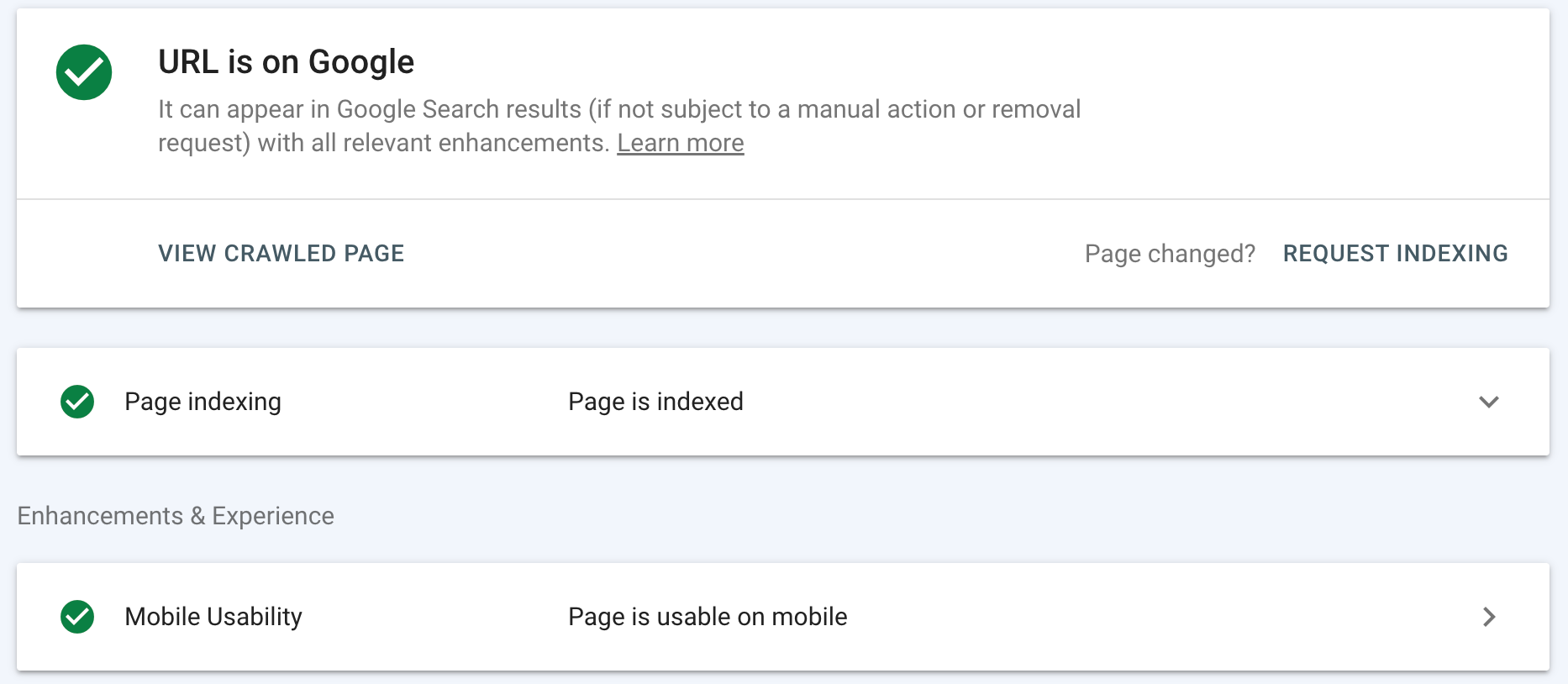
- Google Search Console
What is SEO & Why is SEO Important?
So what exactly is SEO? Well, it stands for Search Engine Optimization, which is a fancy way of saying that it's the process of optimizing your website so that it appears higher in the search engine results page (SERP).
And why is this important? Simple - the higher your website appears in the search engine results, the more likely it is that potential customers will find you!
Why Should You Care About SEO?
Think about it - when was the last time you went to the second or third page of search results when you were looking for something specific online?
Chances are, you didn't - and most people don't either. This means that if your website isn't optimized for search engines, you could be missing out on valuable traffic and potential revenue.
How Search Engines Work
Search engines work by crawling websites, indexing their content, and then ranking them in order of relevance, authority, and user experience.
Relevance refers to how well the content on your website matches the user's search query or search intent.
Authority is determined by the quality and quantity of backlinks pointing to your website from other authoritative sources.
User experience refers to the overall user experience on your website, including factors such as page speed, mobile-friendliness, and user engagement.
Now, I know all of this might sound a bit technical or overwhelming, but don't worry - we'll break it all down for you in simple terms.
The key thing to remember is that search engines work by crawling and indexing websites to determine which pages are the most relevant and valuable for a particular search query.
They use a complex set of algorithms to assess things like keyword usage, content quality, and user experience to determine where your website should rank on the search engine results page.
SEO Keyword Research
One of the most important aspects of good SEO is knowing the relevant keywords you want to rank for. That's where keyword research comes in.
Remember - Having website traffic doesn't matter, having the RIGHT website traffic does.
Search Intent
Let's be honest, when we talk about showing up in the SERP, we are really talking about showing up in a Google search. Google has just over a 93% market share of search queries.
With that in mind, Google ONLY cares about the searcher. Everything in Google's focus is on providing the best search result for a particular search query.
That means everything you do should be focused on the searcher too.
With Google's increasing focus on helpfulness, there are a few things you can focus on to help the searcher and in turn find SEO success:
- Answer Questions - Most search queries are really just questions. If you can provide informative answers to the most asked questions related to your desired keyword concept, you have a great chance at ranking.
- Establish Topical Authority - Google wants to provide authoritative answers to search queries. Create a content strategy around covering every possible topic tangential to your industry - great use of the blog post. Complete topical authority shown on your domain makes you a more trustworthy option in Google's eyes.
- Write Great Content - Google also wants to deliver a world-class experience to the searcher. Google does NOT want to recommend a web page that has poorly written content or a terrible user experience.
Focus on the searcher and you will be rewarded.
Search Volume
You want to find a target keyword for each page that has a good monthly search volume. It's better to shy away from the most popular and competitive terms as your main keyword simply because the more competition, the harder it is to rank for it.
Depending on the niche or industry you serve, a target keyword with a search volume of anywhere from 500-5000 relative searches per month could be beneficial. Remember, the right traffic is what matters.
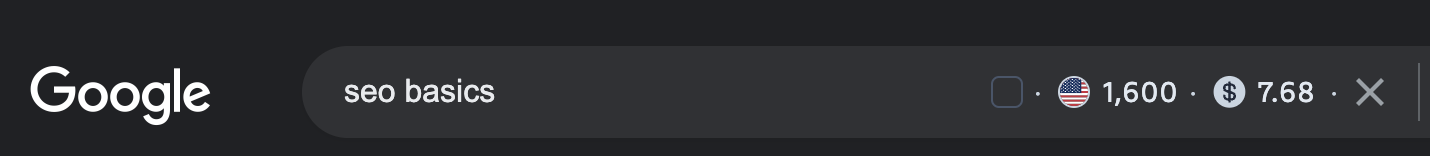
Don't get distracted by less-relevant but higher-volume keywords.
I have clients who do very well off of keywords that only average 250 or so searches per month. They own that keyword and they close a high percentage of leads because they're the top result and the search was relevant to them.
Relevance
Not to beat a dead horse, but we're trying to drive the right traffic to your site. That is relevant to both the search query and your business.
A less popular keyword that's relevant is far and away better than a high-volume keyword that isn't in your service offering.
For example, I have an orthodontic client whose partner recently retired. They had a page on their website about ICONIX Aesthetic Braces that did very well from a traffic standpoint.
However, my client did not personally offer the ICONIX system.
We took the page down.
My client is not a good match for folks looking for ICONIX. His office would only have to field irrelevant inquiries from folks who want what he doesn't have.
Competition
Competitive analysis is a crucial component of any SEO strategy, and it is particularly important when it comes to keyword research. By identifying high-volume, low-competition keywords that your competitors haven't targeted, you can gain a competitive advantage and increase your visibility in the search results.
Some things to think about:
- Analyze your competitors' keywords: Look at the keywords your competitors are targeting. Get an idea of what phrases they are optimizing for and what kind of content they are creating. You can use tools like SEMrush, Ahrefs, or Moz to identify your competitors' top-performing keywords.
- Focus on long-tail keywords: Long-tail keywords are longer, more specific phrases that often have lower search volumes but are easier to rank for. You can avoid direct competition and rank for niche terms that are highly relevant to your target audience.
- Consider search intent: When selecting keywords, it's important to consider the search intent behind them. Are people searching for information, products, or services? By matching your content to the search intent, you can improve your chances of ranking higher in the search results.
- Monitor your competition: Keep an eye on your competition to see what new keywords they are targeting and how they are optimizing their content. This will help you stay ahead of the curve and identify new opportunities that you can take advantage of. I personally love using Spyfu to analyze my competition.
- Don't forget about local search: If you have a local business, it's important to target keywords that are relevant to your geographic location. By focusing on local search terms, you can improve your visibility in local search results and attract more customers from your area.
Keyword Concept
I want to stress the importance of focusing on the keyword concept (or topic cluster) for your landing page or pillar page rather than a specific keyword. You should start with a specific keyword target and use that keyword in your meta title and H1 tag.
However, in my experience, clients get too caught up on specific keywords.
The fact is, keyword rankings jump around constantly. It is not uncommon to see a term rank #1 and then fall out of the rankings entirely just to return to #1 a day later.
How rankings are determined by many factors including the location of the searcher, mobile vs. desktop, competition, and many more.
For the most part, that one keyword isn't making or breaking your page. The reality is, if your SEO is well done, your page will rank for hundreds or maybe thousands of different search terms. Collectively they drive traffic to your site.
I like to think of it sort of like the stock market. If you have one share of a stock and it goes up a dollar, then you've made a dollar. If you have 100 shares of the same stock and the stock price goes up a dollar, now you've made $100.
Keywords work in a similar manner. If you rank for 500 different keywords and all of them bring in traffic, your overall traffic is a lot higher than if you only ranked for one keyword.
Keyword Research Tools
So where do you do all of this keyword research? Good question. There are more tools than I can list that allow you to research search volumes, competition and keyword difficulty, and related keywords.
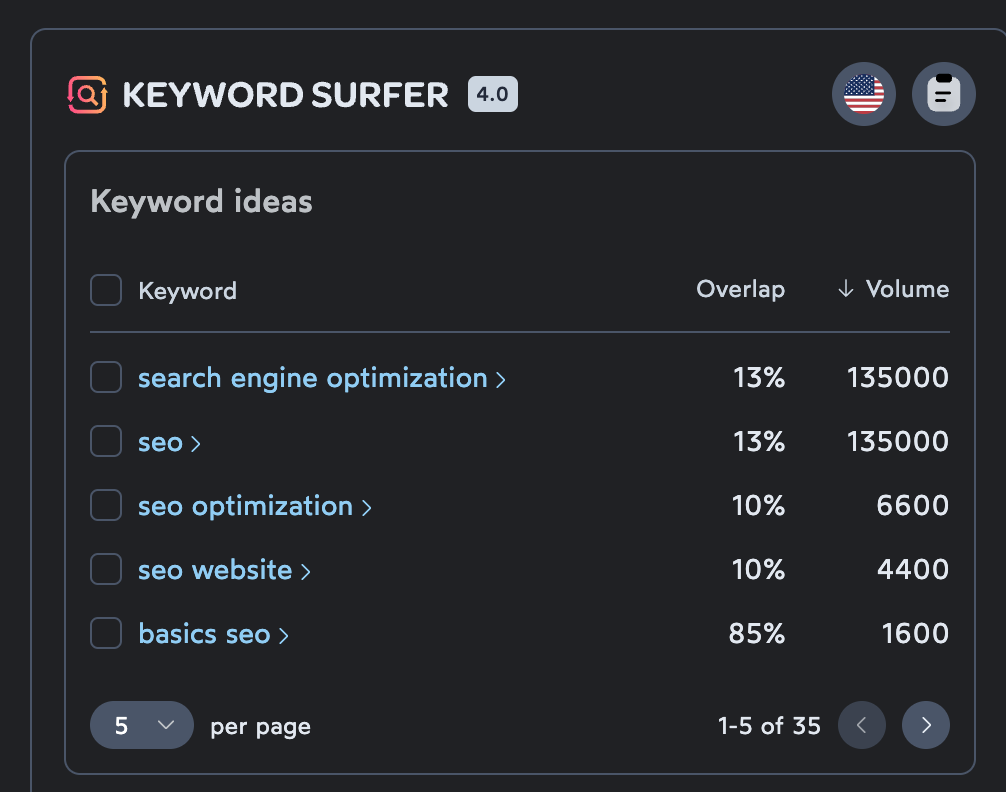
Here is a list of tools that I tend to use on a regular basis.
- Surfer SEO - specifically their Chrome extension
- Google Keyword Planner
- SpyFu
- WordStream
On-Page Optimization
Hopefully, now you've done your keyword research and you have a good list of seed keywords to target on your site. The next step is to actually start optimizing.
Each landing page on your site should be optimized for a different keyword concept to avoid keyword cannibalization.
On-page optimization, as you might have guessed, refers to all of the optimizations that we make on the page itself. The way we structure a page sends lots of signals to Google to help them understand what your page is about.
Let’s take a look.
Page Hierarchy
Google relies on us to help them understand what our site and our pages are about. The way we structure a page can help us communicate to Google what we’re trying to accomplish with our content, what is important to us, and who it’s for.
I like to think of this as the hierarchy of the page. We can use the title tags, H1, H2, and so on to sort of write a narrative that helps Google make more sense of the content on the page.
Title Tags
The SEO title tag is what shows up in the browser tab. Your title tag is not the page headline that shows up at the top of your content.
It’s also the title that populates in the SERP when you show up for a search query.
Your title tag is the single most important on-page optimization (aside from the actual content) you can make. Make sure it has your main keyword.
HTML Headers
An important on-page optimization technique is using meta tags and headers properly. A meta tag is a snippet of HTML code that provides search engines with additional information about your website, while headers (H1, H2, H3) organize your content and signal to search engines what the most important content on the page is.
Your main keyword should be used in your H1 header, the main title of your content. Then, use H2, H3, H4, and so on to hit other related keywords that are important to your topic cluster.
Side note: if logically Google looks at your headers to get an idea of what the page is about thus making it important to include keywords, then it's probably a good idea to try and refrain from having headers that are completely off-topic.
i.e. - I had a client who had an H1 that said “iPad Giveaway" on a page about an academic program. If search engines use the H1 to determine what the page is about, we'd rather it not think the page is about iPad giveaways.
Body Content
Of course, the words on the page matter most. Content should be relevant, well-written, digestible, optimized, and most of all, helpful.
Content is what actually answers a search query and is ultimately why Google will recommend your page to the searcher. Therefore it must be thorough and helpful.
Well-written content is important because if you succeed in optimizing well enough for Google to recommend your content, and a searcher decides to click, you want them to stay on the page once they get there. A high bounce rate can knock you down in the rankings.
This is another reason why you want to make good use of headers to organize content and help readers find what they're looking for quickly. Good use of spacing to spread the content out into digestible chunks is also helpful.
It's also important to avoid duplicate content. Google doesn't like duplicate content from a UX perspective, and it ends up cannibalizing keywords.
Optimizing Content
A quick note about optimizing the content itself - You want your content to be dense with latent semantic topics. Avoid keyword stuffing, but a general rule is to use your main keyword about 1% of the time.
Optimization Tools
There are a number of good AI optimization tools out there that will scour the SERP and give you recommendations of topics you should include in your content to rank for your main keyword.
My personal favorite is MarketMuse, but there are others like Surfer SEO and Clearscope.
Alt Text
Alt text or alt tags are another helpful meta tag. An alt image tag is used to describe an image and is intended to improve the accessibility of a website.
Not only does Google like to see every image have an alt tag for accessibility reasons (remember, they care about being helpful to the searcher), but they can be a good way to work in related keywords.
Since Google reads these when it crawls, they are just additional signals to Google about the topic of the page.
URL Structure
URLs are yet another important factor in how Google sees your page. In general, you want to have well organized and consistent URL structure using hyphens as separators.
Your URL slug should be short, readable, and contain your keyword.
Meta Description
Meta descriptions is the text that shows up in the SERP under you search result that describes what the page is about.
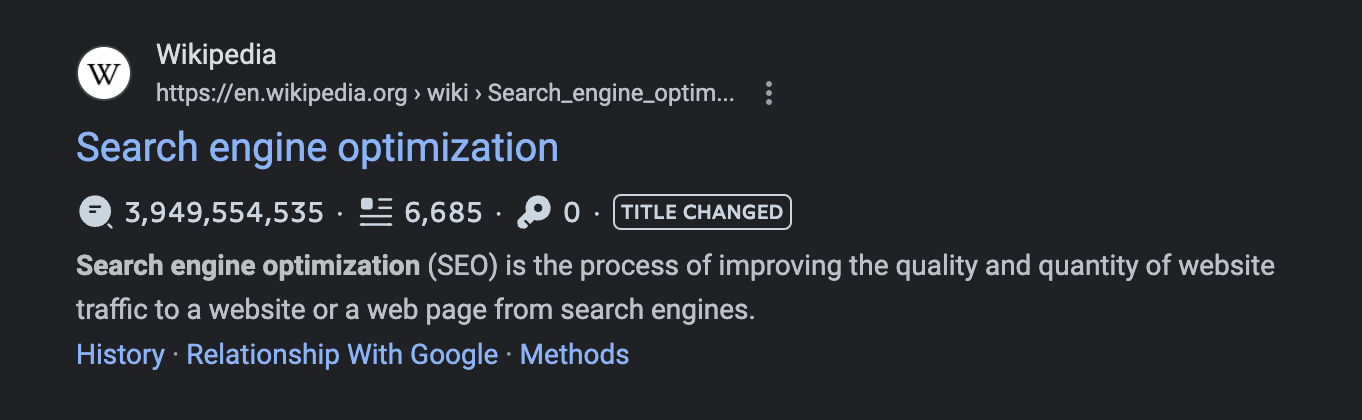
Meta descriptions are not direct ranking factors, in that Google doesn't use them to determine where you show up in the SERP. However, they do show your meta description in the SERP if it makes sense based on the query you're showing up for. A good meta description can entice the searcher to click and click-thru-rate IS a ranking factor.
That said, you should have well-written meta descriptions for all your pages.
Schema Markup
Schema is another important on-page optimization technique that can help your website stand out in search engine results pages.
Schema is a type of structured data markup that makes it easier for search engines to understand the content on your website. This can help improve your website's appearance in search results by displaying rich snippets (such as star ratings, reviews, and images) that make your website more visually appealing to users.
Merkle has a great Schema Markup Generator.
Site Structure
The Importance of Site Structure for SEO
Site structure is a critical aspect of SEO that can significantly impact how search engines crawl and index your website, as well as how users interact with it.
A clear, logical hierarchy of pages makes it easier for both search engines and users to understand how your content is organized, how content topics are related to each other, and how to navigate your website.
Submitting a sitemap to Google is also helpful in helping it make sense of your site and crawl efficiently.
Internal Links
Internal linking is a crucial part of site structure that enables users to navigate around your site and helps search engines crawl your pages more efficiently.
By linking your pages together, you can help distribute link equity throughout your website, making it easier for search engines to understand which pages on your site are the most valuable.
Earlier I mentioned how blogs are a great way to cover tangential topics in order to build topical authority. They also work well to provide SEO support to your landing pages through internal linking.
When you write a blog, link to one or two relevant product or service pages that the blog is related to. Don't overuse internal links on a single page. This breaks down site structure and doesn't help Google make sense of your site.
Breadcrumbs for Navigational Aid
Breadcrumbs are an additional navigational aid that helps users understand their location on your website and the relationship between the pages they are viewing.
Breadcrumbs are also useful for search engines to understand the structure of your website. Using breadcrumbs can help improve the user experience of your website and make it easier for both users and search engines to navigate.
Prioritizing User Experience
When designing your website's structure, it's important to prioritize user experience (always be helpful). Having a clear, easy-to-navigate site structure will not only help your SEO but will also make it easier for users to find what they are looking for on your website.
Link Building
Google's algorithm still sees external links as a very important ranking factor. That is, links from other website pointing back to your site.
The general idea behind external links is that they are a vote of confidence for the content on your site. If others found what you've written valuable enough to link to, then it must be good and you must be authoritative.
In Google's ideal world, all of this link building happens organically. People find your content, like it, and then link to it.
Google has said they don't like ANYTHING that could be considered link manipulation. That said, there are different ways that people go about building links from outreach to collaboration to guest blogging.
I won't go further into link building, just know that external links are good, especially if they are from an authoritative and/or industry-relevant site.
Technical SEO
Technical SEO refers to the technical aspects of a website that can impact its search engine visibility. While it may not be the most glamorous aspect of SEO, it's essential for ensuring that your website performs well in the SERP.
Some of the technical elements of SEO include site speed, mobile-friendliness, and header response. Other technical aspects may include managing the website's back-end architecture to enable faster page loads, updating sitemaps, and optimizing robots.txt files.
It's also important to make sure you have proper redirects in place if you change a URL slug or delete a page. Link juice can pass through a redirect and you don't ever want a user to land on a non-existent page.
Examples of Technical SEO Optimizations
- Compressing images to reduce page load time
- Improving server response time
- Using responsive design to create a mobile-friendly website
- Creating a sitemap to help search engines crawl your website more efficiently
- Optimizing your robots.txt file for better search engine crawling
Local SEO
I won't go in-depth on local SEO, but it's important to touch on. For a local business, local focus is far more important since that's where their business is coming from.
Without spending too much time on it, just know the following…
- Make sure you have a Google Business Profile (GBP)
- Make sure to select the most relevant business category
- Optimize your site for your location along with your product/service
- Ask for reviews
Analytics and Reporting
Analytics is another thing I won't go into in depth here. But there are some things to keep in mind:
- Remember that individual keyword rankings aren't the end-all be-all.
- Traffic isn't either. The right traffic is far more important.
- However, growth in impressions and organic traffic are good signs.
- Pay attention to Click-thru-rate (CTR).
- If bounce rate is high, make content and UX better.
Analytics Tools
- Google Search Console - It's free and it gives you great information such as impressions, clicks, search queries you showed up for, and CTR. Google Search Console can give you an idea of what you're showing up for in organic search results.
- Google Analytics - GA is also free and provides you with a better look at user acquisition and demographic info.
- Rank Tracker - I know I said that individual rankings aren't the most important thing. However, if you've made an effort to optimize a page for a specific topic, you should be tracking it to see how you did and inform further optimizations. There are a ton of rank traders out there. My favorite affordable option is Serpfox.
If you're just starting out and putting forth your own SEO efforts, you can get a ton of good data from these three tools. Between Google Search Console and Google Analytics, you can get a ton of user information.
As you grow, you'll likely want a way to analyze backlinks, but you can find basic backlinking data in GSC too.
Conclusion
SEO is a never-ending battle. That's why most businesses end up hiring SEO firms to do the work for them. But I promise you can get a long way on your own SEO efforts.
My hope is that with this guide of SEO fundamentals, you can form an SEO strategy to own the organic search results, reach potential customers and grow your business.
SEO is only one piece of a full digital marketing strategy that might include paid search like Google Ads or social media ads. There are always ways to move the needle. Good luck on your path to becoming an SEO expert!